The potential use of glucose oxidase-imprinted polymer-coated electrodes for biofuel cells†
Abstract
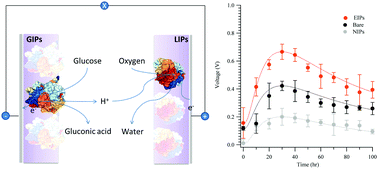
Molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs) have proven useful for the surface immobilization of enzymes via the complementary cavities they present. Immobilization in this manner may prove useful in maintaining enzymatic efficacy. In biofuel cell applications, the thickness of an imprinted polymer layer coated on the electrode can be effectively controlled to yield the desired electron conductivity. In this work, glucose oxidase (GOx) and laccase (Lc) were imprinted on the surfaces of the anode and cathode of a biofuel cell at concentrations of 0.1 and 0.02 mg mL−1, respectively, using a poly(ethylene-co-vinyl alcohol) matrix. The effectiveness of imprinting was maximized by using 32 mole% ethylene and an enzyme concentration of 0.1 wt%. The surface morphology of the imprinted cavities and their interactions with the imprinted proteins were investigated by atomic force microscopy, revealing both the surface morphology of the imprinted cavities and the attractive force between the protein and the imprinted matrix. Finally, the output of the enzymatic biofuel cells was measured. Immobilization of the enzymes using the MIP electrodes gave substantially improved performance, compared to passive adsorption on either polymer-coated or bare electrodes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...