Morphological and in vitro evaluation of programmed cell death in MCF-7 cells by new organoruthenium(ii) complexes†
Abstract
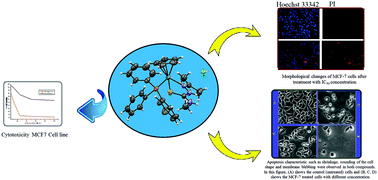
Cyclopentadienyl ruthenium(II) thiosemicarbazone complexes with the general formula [Ru(η5-C5H5)(Ac-tsc)PPh3]·Cl (1), [Ru(η5-C5H5)(Ac-mtsc)PPh3]·Cl (2), [Ru(η5-C5H5)(Ac-etsc)PPh3]·Cl (3) and [Ru(η5-C5H5)(Ac-ptsc)PPh3] (4) were synthesized and characterized by various spectroscopic techniques (1H NMR, 13C NMR, IR and UV-vis). The molecular structures of the representative complexes 2 and 4 were studied by single-crystal X-ray diffraction. The interactions of all the ligands and complexes with calf thymus DNA (CT-DNA) and bovine serum albumin (BSA) were studied using UV-vis and fluorescence emission spectroscopy. The results of binding studies revealed that the effective binding potentials of the complexes were higher than those of their parent ligands. All the new complexes 1–4 were investigated for their in vitro cytotoxic activity against MCF-7 human breast cancer cell line. All the complexes significantly inhibited cell proliferation in MCF-7 cells in a dose-dependent manner. Cytological observations via an inverted phase contrast microscope and a Hoechst 33342/PI dual-staining assay showed typical apoptotic morphology of cancer cells upon treatment with complexes 2 and 3. It can thus be suggested that the complexes 2 and 3 are modulated by apoptosis. The findings of the present study indicated that complexes 2 and 3 may become potent drugs for the treatment of cancer-related diseases only after further investigation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...