Fabrication of 4-aminophenol sensor based on hydrothermally prepared ZnO/Yb2O3 nanosheets†
Abstract
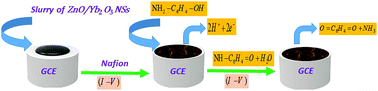
In this study, a facile hydrothermal process was used to prepare the NSs of ZnO/Yb2O3 in an alkaline medium (pH ∼ 10.5), at a low temperature. The calcined NSs were characterized by Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), ultraviolet visible spectroscopy (UV/vis), field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS), transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and powder X-ray diffraction (XRD). A thin layer of NSs was coated on a glassy carbon electrode (GCE) with the help of a nafion conducting binder to be used as a sensor. This assembled sensor was implemented to the successful detection of 4-AP and exhibited good sensitivity (5.063 μA μM−1 cm−2) and a low detection limit (DL = 0.019 ± 0.001 nM at a signal to noise ratio of 3). The calibration plot (attained at a potential of +1.0 V) is linear (r2 = 0.9836) in the concentration range of 0.1 nM to 0.1 mM of 4-AP. Therefore, the chemical sensor fabricated with ZnO/Yb2O3 NSs may be a promising sensitive chemical sensor in a reliable I–V method for the effective detection of hazardous and carcinogenic chemicals in environmental and healthcare sectors on broad scales.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...