Halide assisted formation of polymeric ethylenediaminetetraacetato lead(ii) complexes†
Abstract
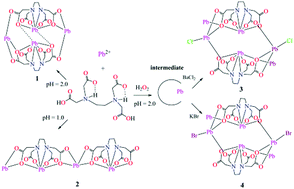
Insoluble lead(II) ethylenediaminetetraacetate isomers [Pb2(EDTA)(H2O)]2n (1) and [Pb4(EDTA)2]n·2nH2O (2) and allomers Pbn[Pb(EDTA)Pb(H2O)X]2n·2nH2O (X = Cl, 3 and Br, 4) are isolated from the reactions of lead nitrate with ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid in acidic solution (H4EDTA = ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid). The four complexes are fully characterized via elemental analysis, FT-IR spectroscopy, thermogravimetric analyses, solid state 13C NMR spectroscopy and X-ray crystal structure analyses. Topological analyses of complexes 2 and 3(4) show unusual (6,8)-connected 2-nodal and (4,5,6)-connected 3-nodal network topologies, respectively. The insertions of chloride and bromide in 3 and 4, respectively, give new polymeric lead–EDTA complexes. Products 3 and 4, which are obtained at room temperature, show a significant halide-assisted formation effect of insoluble ethylenediaminetetraacetato lead(II) complexes, which is supported by solid state NMR and X-ray crystal structure analyses.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...