New polytriazoleimides containing green synthesized titanium dioxide using Artemisia pallens plant extract: optical, dielectric, thermal and mechanical properties†
Abstract
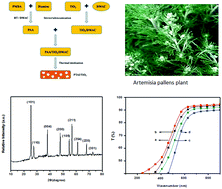
A novel aromatic diamine containing a pyridine pendant group, 1,2,3-triazole ring and ether linkage was synthesized by ‘click reaction’ in the presence of Cu(I) catalyst. Titanium dioxide (TiO2) was introduced in poly(amic acid) to prepare poly(triazole-imide) (PTAI) nanocomposite film by typical solution casting and thermal imidization method. The TiO2 was prepared from Artemisia pallens plant extract by sol–gel method. The structure of the PTAI was confirmed by FT-IR and NMR analyses. The morphologies of TiO2 and PTAI as well as those of PTAI/TiO2 nanocomposites were investigated by X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy and transmission electron microscopy. PTAI/TiO2 nanocomposite films containing different amounts of TiO2 (0–15 wt%) were compared in terms of their morphologies and thermal, mechanical and optical properties. The tensile strength and elongation at break decreased with an increase in the TiO2 percentage. Furthermore, the incorporation of TiO2 in the polymer matrix significantly improved the glass transition temperature (260–283 °C) and thermal stability (T5% were found to be in the range of 483–540 °C) of the composite films in terms of their char yield (found to be in the range of 49.3–60.1 at 800 °C). The dielectric constant (in the range of 3.12–4.10 at 1 MHz) and dielectric loss (in the range of 0.15–0.30 at 1 MHz) increased with an increase in the content of TiO2. This effective approach shows a potential application in fabricating multifunctional polymer-based composites.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...