The development of small-molecule modulators for ClpP protease activity
Abstract
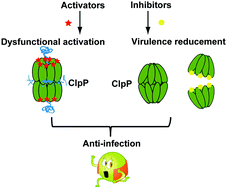
The global spread of antibiotic resistance among important human pathogens emphasizes the need to find new antibacterial drugs with a novel mode of action. The ClpP protease has been shown to demonstrate its pivotal importance to both the survival and the virulence of pathogenic bacteria during host infection. Deregulating ClpP activity either through overactivation or inhibition could lead to antibacterial activity, declaiming the dual molecular mechanism for small-molecule modulation. Recently, natural products acyldepsipeptides (ADEPs) have been identified as a new class of antibiotics that activate ClpP to a dysfunctional state in the absence of cognate ATPases. ADEPs in combination with rifampicin eradicate deep-seated mouse biofilm infections. In addition, several non-ADEP compounds have been identified as activators of the ClpP proteolytic core without the involvement of ATPases. These findings indicate a general principle for killing dormant cells, the activation and corruption of the ClpP protease, rather than through conventional inhibition. Deletion of the clpP gene reduced the virulence of Staphylococcus aureus, thus making it an ideal antivirulence target. Multiple inhibitors have been developed in order to attenuate the production of extracellular virulence factors of bacteria through covalent modifications on serine in the active site or disruption of oligomerization of ClpP. Interestingly, due to the unusual composition and activation mechanism of ClpP in Mycobacterium tuberculosis, mycobacteria are killed by ADEPs through inhibition of ClpP activity rather than overactivation. In this short review, we will summarize recent progress in the development of small molecules modulating ClpP protease activity for both antibiotics and antivirulence.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...