Electrophoretic cytometry of adherent cells†
Abstract
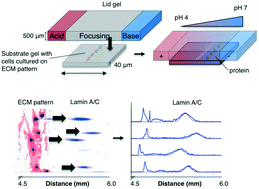
Cell–matrix and cell–cell interactions influence intracellular signalling and play an important role in physiologic and pathologic processes. Detachment of cells from the surrounding microenvironment alters intracellular signalling. Here, we demonstrate and characterise an integrated microfluidic device to culture single and clustered cells in tuneable microenvironments and then directly analyse the lysate of each cell in situ, thereby eliminating the need to detach cells prior to analysis. First, we utilise microcontact printing to pattern cells in confined geometries. We then utilise a microscale isoelectric focusing (IEF) module to separate, detect, and analyse lamin A/C from substrate-adhered cells seeded and cultured at varying (500, 2000, and 9000 cells per cm2) densities. We report separation performance (minimum resolvable pI difference of 0.11) that is on par with capillary IEF and independent of cell density. Moreover, we map lamin A/C and β-tubulin protein expression to morphometric information (cell area, circumference, eccentricity, form factor, and cell area factor) of single cells and observe poor correlation with each of these parameters. By eliminating the need for cell detachment from substrates, we enhance detection of cell receptor proteins (CD44 and β-integrin) and dynamic phosphorylation events (pMLCS19) that are rendered undetectable or disrupted by enzymatic treatments. Finally, we optimise protein solubilisation and separation performance by tuning lysis and electrofocusing (EF) durations. We observe enhanced separation performance (decreased peak width) with longer EF durations by 25.1% and improved protein solubilisation with longer lysis durations. Overall, the combination of morphometric analyses of substrate-adhered cells, with minimised handling, will yield important insights into our understanding of adhesion-mediated signalling processes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...