Vasorelaxant activity of twenty-one physiologically relevant (poly)phenolic metabolites on isolated mouse arteries
Abstract
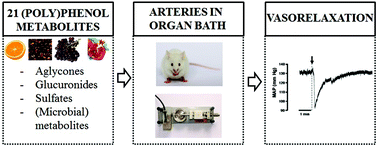
Polyphenols are beneficial for health, but are metabolised after consumption. We compared the vasorelaxant capacity of twenty-one physiologically relevant polyphenol metabolites in isolated mouse arteries. Hesperetin, urolithins and ferulic acid-4-O-sulfate – not their glucuronidated forms or ferulic acid – caused vasorelaxation. Therefore, we advise the use of relevant conjugates in future mechanistic research.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...