The hypoglycemic and antioxidant effects of polysaccharides from the petioles and pedicels of Euryale ferox Salisb. on alloxan-induced hyperglycemic mice
Abstract
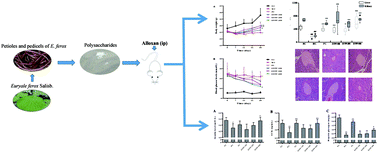
The present study investigated the potential hypoglycemic and antioxidant effects of polysaccharides extracted from the petioles and pedicels of Euryale ferox Salisb. (EFPP) on alloxan-induced hyperglycemic mice. The EFPP had a total carbohydrate of 65.72 ± 2.81%, uronic acid of 4.56 ± 0.62% and protein of 0.58 ± 0.12%, with an average molecular weight from 1.02 kDa to 11.45 kDa and monosaccharide composition of Man, GlcA, Rha, Glc, Gal and Ara at a molar ratio of 0.12 : 0.01 : 9.57 : 0.41 : 1.00 : 0.24. Administration with EFPP, especially high dose EFPP, was beneficial to reverse body weight loss, reduce blood glucose levels, enhance serum insulin levels, improve oral glucose tolerance, increase hepatic glycogen content and GCK activity, and modulate the mRNA expression of GCK in the liver. Meanwhile, EFPP had protective effects against alloxan-induced oxidative injury in mice, via increasing the activities of SOD, CAT and GSH-Px and decreasing the MDA contents in the liver and kidney of the mice. EFPP ameliorated the damage in pancreas, kidney and liver tissues, which was confirmed by histopathological observation. The results suggested that EFPP possess hypoglycemic and antioxidant activities, and could be a potential source of natural hypoglycemic and antioxidant agents for functional foods or complementary medicines.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...