Raspberry differentially improves age-related declines in psychomotor function dependent on baseline motor ability
Abstract
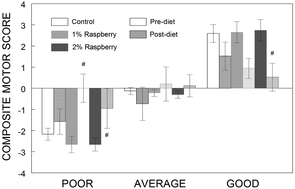
Among older adults, falls are a leading cause of distress, pain, injury, loss of confidence, and ultimately, loss of independence and death. Previous studies in our laboratory have demonstrated that berry supplementation improves the age-related declines in balance, muscle strength, and coordination that often lead to falls, even when initiated later in life. The purpose of this study was to explore the interaction between baseline motor performance and the daily intake of raspberry required to improve/preserve motor function. Aged male F344 (17 mo) rats were tested for baseline (pre-test) balance, muscle strength, and coordination, and divided into good, average, and poor performers based on their motor composite score. Rats in each category were fed with either a control, 1%, or 2% raspberry-supplemented diet for 8 weeks and then retested (post-test). Poor performers fed with 1% or 2% raspberry had higher post-test composite scores (p < 0.05), while 2% raspberry lowered post-test composite scores in the good performers (p < 0.05), compared to control-fed rats. 1% and 2% raspberry appeared to preserve the performance of good performers and improve the performance of poor performers on plank walking (p < 0.05), while 2% raspberry improved post-test grip strength of the poor performers (p < 0.05). Additionally, rats with lower post-diet composite scores had higher levels of serum IL-1β levels (r = −0.347, p < 0.05). These findings identified poor performers as being the most likely to benefit from daily consumption of ½–2 cups of raspberry to improve/preserve motor function. Therefore, increased raspberry consumption may reduce fall risk, extend independence, and improve quality of life in the aging population.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Berry Health Benefits Symposium


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...