The protective effects of Cichorium glandulosum seed and cynarin against cyclophosphamide and its metabolite acrolein-induced hepatotoxicity in vivo and in vitro
Abstract
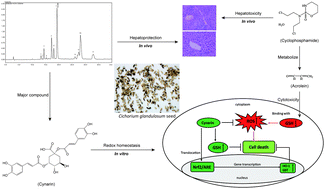
Cyclophosphamide (CP) is a widely utilized chemotherapy drug. CP and its metabolite, acrolein, could induce hepatotoxicity. In this study, Cichorium glandulosum seed (CGS) effectively mitigated CP-induced hepatotoxicity in mice. Protection of cynarin, the major compound of CGS, against acrolein cytotoxicity in HepG2 cells was studied. Pretreatment with cynarin could improve cell survival against acrolein cytotoxicity. Cynarin restored the balance of glutathione (GSH) and reactive oxygen species (ROS), and inhibited mitochondrial depolarization. The kinetics of Nrf2 expression in cytosolic and nuclear fractions were observed after acrolein exposure. Intracellular Nrf2 expression was triggered within 6 h of exposure but did not translocate to the nucleus. Cynarin pretreatment ameliorated the expression and activity of GSH S-transferase and triggered Nrf2 nuclear translocation. In conclusion, treatment with CGS and cynarin protects liver injury against CP and acrolein hepatotoxicity via improvement of GSH activity and activation of the Nrf2 pathway.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...