Graphitic carbon nitride-based nanocomposites as visible-light driven photocatalysts for environmental purification
Abstract
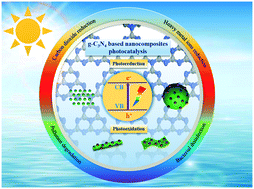
Graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4) has attracted enormous attention since it was first reported as a metal-free conjugated semiconductor photocatalyst that could realize the direct conversion of solar energy to chemical energy. Due to its abundant resources, facile synthesis methods, appealing electronic structure combined with a medium band gap (2.7 eV) and high physicochemical stability, g-C3N4 has quickly became a hotspot in photocatalysis fields. However, practical applications are still hindered by several obstacles, such as the high recombination rate of photo-generated electron–hole pairs, low electronic conductivity, small specific surface area and lack of visible light absorption above 460 nm. Hybridizing g-C3N4 with other components has been proved as a promising solution. On account of the great dedication and significant progress in exploitation of g-C3N4-based nanocomposites, we herein present an updated and comprehensive review on the recent advances in different dimensional g-C3N4-based nanocomposites. These specially structured nanocomposites, such as g-C3N4 nanotube-, g-C3N4 nanofiber-, g-C3N4 nanosheet- and g-C3N4 nanosphere-based nanocomposites can be applied in a number of environmentally-relevant fields such as pollutant degradation, heavy metal ions reduction, bacterial disinfection and CO2 reduction. This review primarily focuses on fabrication methods, properties, photocatalytic mechanisms and applications of different dimensional g-C3N4-based nanocomposites and ends with a brief summary and perspective.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Environmental Science: Nano 2017 Most Downloaded Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...