The influence of the ancillary ligand on the potential of cobalt(iii) complexes to act as chaperones for hydroxamic acid-based drugs†
Abstract
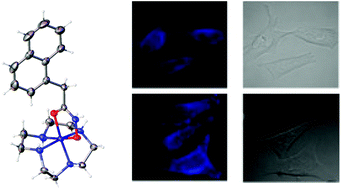
Cobalt(III) chaperones are a promising class of bioreductive prodrugs under investigation for the delivery of cytotoxic ligands to hypoxic solid tumours. Here we investigate a series of cobalt complexes as chaperones for hydroxamic acid ligands, comparing the properties of the cyclic cyclen (1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane) ancillary ligand with the tripodal tpa (tris-(2-pyridylmethyl)amine) and tren (tris-(2-aminoethyl)amine). A small library of complexes containing several different hydroxamic acids, including the MMP inhibitor Marimistat and the fluorescent ligand C343haH2, were prepared and their pKa values, reduction potentials, and in some cases X-ray crystal structures, were determined. The antiproliferative actitivity of the series was evaluated against DLD-1 colon cancer cells and the cellular accumulation of the fluorescent C343haH2 complexes was monitored by ICPMS and confocal fluorescence microscopy, revealing that the nature of the ancillary ligand significantly influences the complexes’ properties, cytotoxicity and cellular distribution.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...