Adamantyl metal complexes: new routes to adamantyl anions and new transmetallations†
Abstract
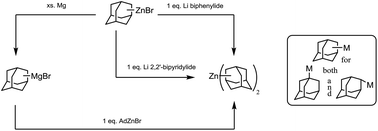
New routes to 1- and 2-adamantyl anion equivalents are described, starting from commercially available 1- and 2-adamantylzinc bromides and employing reducing metals (Mg; Li). Adamantylmagnesium bromides (both 1-AdMgBr and 2-AdMgBr) can reliably be produced via reaction of the corresponding adamantylzinc bromides with excess magnesium metal. Reactions of adamantylzinc bromides with stoichiometic lithium biphenylide or lithium 2,2′-bipyridylide afford the new diadamantylzinc species, 1-Ad2Zn and 2-Ad2Zn, isolable free of solvent and salt impurities. Addition of 2,2′-bipyridine (bipy) leads to the crystalline adducts 1-Ad2Zn(bipy) and 2-Ad2Zn(bipy), which were structurally characterized. The resulting adamantyl anions were used in order to generate the first adamantyl complexes of mercury (1- and 2-Ad2Hg), gold (1- and 2-AdAu(PPh3), 1- and 2-AdAu(PCy3)) and bismuth (2-Ad2BiBr), of which 1- and 2-Ad2Hg, 2-AdAu(PPh3), 2-AdAu(PCy3), and 2-Ad2BiBr were isolated. These include the first structurally characterized unsupported 2-adamantyl metal complexes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...