Insights into influence of nanoparticle size and metal–support interactions of Cu/ZnO catalysts on activity for furfural hydrogenation
Abstract
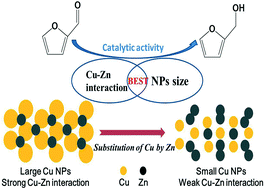
Cu/ZnO catalysts primarily derived from aurichalcite with Cu/Zn = 0.4–1.1 (mol/mol) were prepared via “decreased pH” coprecipitation method and introduced in hydrogenation of furfural to furfuryl alcohol. The “precursor effect” was clearly confirmed and the catalyst with a Cu/Zn = 0.8 provided the best conversion and TOF. Catalysts were characterized via XRD, FT-IR, N2O titration, TEM, H2-TPR, XPS and AES. The size of Cu nanoparticles and Cu–ZnO interactions were systematically investigated and were found to remarkably influence catalytic activity of the catalysts. Consequently, the best catalytic performance for the catalyst with Cu/Zn = 0.8 was due to the suitable Cu particle size (8 nm) and strong metal–support interactions (SMSI), acting as the Cu–ZnO synergy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...