p-Cu2S/n-ZnxCd1−xS nanocrystals dispersed in a 3D porous graphene nanostructure: an excellent photocatalyst for hydrogen generation through sunlight driven water splitting†
Abstract
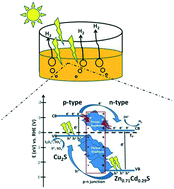
A cocktail strategy to design composite semiconductor photocatalysts for high performance sunlight driven photocatalytic water splitting for hydrogen generation was developed. It includes band gap tuning, p–n junction formation, and dispersion of p–n junctions in a 3D well-connected conductive support. An over fourfold improvement in the hydrogen evolution rate was achieved by Zn0.71Cd0.29S over CdS, 13 vs. 2.7 μmol h−1 under irradiation with simulated sunlight at 100 mA cm−2, through compositing and thus band gap tuning. A further improvement, from 13 to 43.4 μmol h−1, was achieved by compositing p-type Cu2S with n-type Zn0.71Cd0.29S to form p-Cu2S/n-Zn0.71Cd0.29S composite nanocrystals, to greatly enhance charge separations. Even more improvements were realized, boosting the hydrogen evolution rate up to 60.1 μmol h−1, by dispersing the p-Cu2S/n-Zn0.71Cd0.29S composite nanocrystals in a 3D, highly conductive porous graphene nanostructure. The porous graphene nanostructure attracts the photo-induced electrons to further improve the involved charge separation. A one-order of magnitude improvement in hydrogen generation over CdS, the best known sunlight responsive photocatalyst for water splitting, was thus achieved with this cocktail material design. The highest specific hydrogen evolution rate achieved, 1202 μmol g−1 h−1, is among the highest for metal sulfide based sunlight driven water splitting.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...