Controlling N2O formation during regeneration of NOx storage and reduction catalysts: from impact of platinum-group metal type to rational utilization†
Abstract
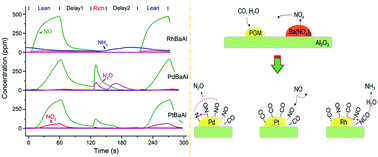
Herein, we report an effective strategy for minimization of N2O emissions based on elucidating the impact of the type of platinum-group metals (PGMs = Pt, Pd, or Rh) on by-product formation during regeneration of PGM–BaO/Al2O3 catalysts. The significant differences in N2O or NH3 formation were thoroughly investigated from the perspective of an in situ reaction. Kinetic analysis of NO reduction by CO shows different turnover frequency and apparent activation energy values over these catalysts. The results reveal that the apparent kinetics is dependent on the type of platinum-group metal chosen. In situ DRIFTS data indicate that the unique adsorption behaviors of reactants via which they access each PGM essentially determine their individual reaction kinetics. The preferential adsorption of NO or CO molecules on the PGM surface controls the dominant intermediate (NOad/Nad, COad, or NCOad) species, which is a major factor responsible for various yields of N2O and NH3 during the rich period. Finally, a feasible strategy has been proposed via optimizing catalyst formulation to effectively control the N2O emissions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...