Solvent effects on the excited-state double proton transfer mechanism in the 7-azaindole dimer: a TDDFT study with the polarizable continuum model†
Abstract
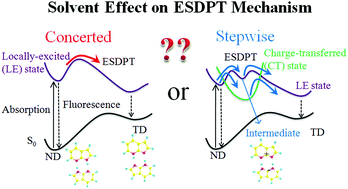
Solvent effects on the excited-state double proton transfer (ESDPT) mechanism in the 7-azaindole (7AI) dimer were investigated using the time-dependent density functional theory (TDDFT) method. Excited-state potential energy profiles along the reaction paths in a locally excited (LE) state and a charge transfer (CT) state were calculated using the polarizable continuum model (PCM) to include the solvent effect. A series of non-polar and polar solvents with different dielectric constants were used to examine the polarity effect on the ESDPT mechanism. The present results suggest that in a non-polar solvent and a polar solvent with a small dielectric constant, ESDPT follows a concerted mechanism, similar to the case in the gas phase. In a polar solvent with a relatively large dielectric constant, however, ESDPT is likely to follow a stepwise mechanism via a stable zwitterionic intermediate in the LE state on the adiabatic potential energy surface, although inclusion of zero-point vibrational energy (ZPE) corrections again suggests the concerted mechanism. In the meantime, the stepwise reaction path involving the CT state with neutral intermediates is also examined, and is found to be less competitive than the concerted or stepwise path in the LE state in both non-polar and polar solvents. The present study provides a new insight into the experimental controversy of the ESDPT mechanism of the 7AI dimer in a solution.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...