Cu0-Loaded organo-montmorillonite with improved affinity towards hydrogen: an insight into matrix–metal and non-contact hydrogen–metal interactions†
Abstract
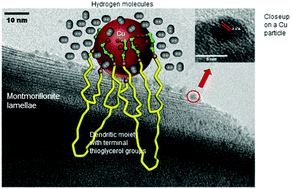
Copper-loaded organo-montmorillonite showed improved affinity towards hydrogen under ambient conditions. Clay ion exchange with a propargyl-ended cation followed by thiol–yne coupling with thioglycerol resulted in a porous structure with a 6 fold higher specific surface area, which dramatically decreased after copper incorporation. X-ray diffraction and photoelectron spectrometry, nuclear magnetic resonance (1H and 13C) and CO2-thermal programmed desorption revealed strong sulfur:Cu0 and oxygen:Cu0 interactions. This was explained in terms of structure compaction that ‘traps’ Cu0 nanoparticles (CuNPs) and reduces their mobility. Transmission electron microscopy showed predominant 1.0–1.5 nm CuNPs. Hydrogen capture appears to involve predominantly physical interaction, since differential scanning calorimetry measurements gave low desorption heat and almost complete gas release between 20 °C and 75 °C. Possible hydrogen condensation within the compacted structure should hinder gas diffusion inside CuNPs and prevent chemisorption. These results allow safe hydrogen storage with easy gas release to be envisaged even at room temperature under vacuum. The reversible capture of hydrogen can be even more attractive when using natural inorganic supports and commercial plant-derived dendrimers judiciously functionalized, even at the expense of porosity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...