Spectroscopic characterization of the on-surface induced (cyclo)dehydrogenation of a N-heteroaromatic compound on noble metal surfaces
Abstract
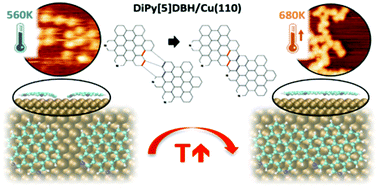
New nanoarchitectures can be built from polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) by exploiting the capability of some metal surfaces for inducing cyclodehydrogenation reactions. This bottom-up approach allows the formation of nanostructures with a different dimensionality from the same precursor as a consequence of the diffusion and coupling of the PAHs adsorbed on the surface. In this work we present a thorough study, by means of a combination of X-ray photoemission spectroscopy, near-edge X-ray absorption fine structure and scanning tunneling microscopy with first principle calculations of the structural and chemical transformations undergone by pyridyl-substituted dibenzo[5]helicene on three coinage surfaces, namely Cu(110), Cu(111) and Au(111). Upon annealing, on-surface chemical reactions are promoted affecting the adsorbate/substrate and the molecule/molecule interactions. This thermally induced process favours the transformation from diffusing isolated molecules to polymeric nanographene chains and finally to N-doped graphene.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...