Efficient multicolor tunability of ultrasmall ternary-doped LaF3 nanoparticles: energy conversion and magnetic behavior†
Abstract
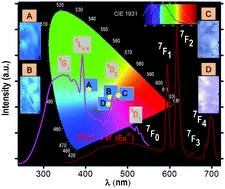
Luminescence-tunable multicolored LaF3:xCe3+,xGd3+,yEu3+ (x = 5; y = 1, 5, 10, and 15 mol%) nanoparticles have been synthesized via a low cost polyol method. Powder X-ray diffraction and high-resolution transmission electron microscopy studies confirm the hexagonal phase of the LaF3:xCe3+,xGd3+,yEu3+ nanophosphors with average sizes (oval shape) ranging from 5 to 7 nm. Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy analyses show the uniform distribution of Ce3+, Gd3+, and Eu3+ dopants in the LaF3 host matrix. The photoluminescence spectra and electron paramagnetic resonance measurements guarantee the presence of Eu2+, corroborated through DC susceptibility measurements of the samples displaying paramagnetic behavior at 300 K, whereas weak ferromagnetic ordering is shown at 2 K. The non-radiative energy transfer processes from the 4f(2F5/2) → 5d state (Ce3+) to the intraconfigurational 4f excited levels of rare earth ions and simultaneous emissions in the visible region from the 4f65d1 (Eu2+) and 5D0 (Eu3+) emitting levels, leading to overlapped broad and narrow emission bands, have been proclaimed. The energy transfer mechanism proposes involvement of the Gd3+ ion sub-lattice as the bridge and finally trapping by Eu2+/3+, upon excitation of the Ce3+ ion. The calculation of experimental intensity parameters (Ω2,4) has been discussed and the highest emission quantum efficiency (η = 85%) of the Eu3+ ion for the y = 10 mol% sample is reported. The advantageous existence of the Eu2+/Eu3+ ratio along with variously doped nanomaterials described in this work, results in tunable emission color in the blue-white-red regions, highlighting the potential application of the samples in solid-state lighting devices, scintillation devices, and multiplex detection.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...