Titanium dioxide nanotube membranes for solar energy conversion: effect of deep and shallow dopants†
Abstract
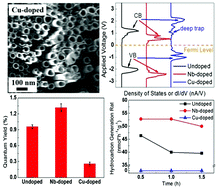
Nanostructured titanium dioxide (TiO2) has been intensively investigated as a material of choice for solar energy conversion in photocatalytic, photoelectrochemical, photovoltaic, and other photosensitized devices for converting light into chemical feedstocks or electricity. Towards management of light absorption in TiO2, while the nanotubular structure improves light absorption and simultaneous charge transfer to mitigate problems due to the indirect bandgap of the semiconductor, typically dopants are used to improve light absorption of incident solar irradiation in the wide bandgap of TiO2. While these dopants can be critical to the success of these solar energy conversion devices, their effect on photophysical and photoelectrochemical properties and detailed photokinetics are relatively under-studied. Here, we show the effect of deep and shallow metal dopants on the kinetics of photogenerated charged carriers in TiO2 and the resulting effect on photocatalytic and photoelectrochemical processes using these nanotube membranes. We performed a detailed optical, electronic, voltammetry and electrochemical impedance study to understand the effect of shallow and deep metal dopants (using undoped and niobium- and copper-doped TiO2 nanotubes) on light absorption, charge transport and charge transfer processes. Using wireless photocatalytic methylene blue degradation and carbon dioxide reduction, and wired photoelectrochemical device measurements, we elucidate the effect of different dopants on solar-to-fuel conversion efficiency and simultaneously describe the photokinetics using a model, to help design better energy conversion devices.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...