Order–disorder phase transition induced by proton transfer in a co-crystal of 2,4-dichlorobenzoic acid and trimethylamine N-oxide†
Abstract
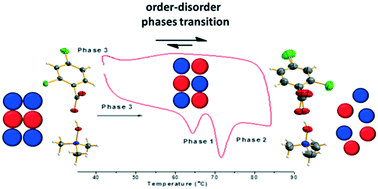
A crystalline binary adduct between trimethylamine N-oxide (TMANO) and 2,4-dichlorobenzoic acid (2,4-DCBA) molecules was obtained by slow evaporation from acetonitrile. The obtained molecular complex is formed by a racemic mixture of molecular complexes crystallizing in the orthorhombic space group Pbca. An exhaustive analysis of the temperature dependence of the cell parameters and the behavior of the acidic hydrogen position and carboxylate group was performed by single crystal and powder X-ray diffraction, FT-IR spectroscopy and theoretical calculations. The molecular system was thermally characterized, subsequently demonstrating an order–disorder transition. Finally, the intermolecular interactions were analyzed via Hirshfeld surface analysis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...