Syntheses, structures and luminescence properties of five coordination polymers based on designed 2,7-bis(4-benzoic acid)-N-(4-benzoic acid) carbazole†
Abstract
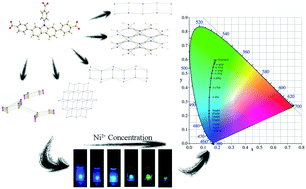
Herein we report five porous luminescent coordination polymers (CPs), namely, [Zn3(L27)2(DMA)6(H2O)4]n (TCZ-001), [Zn3(L27)2(DMA)6(CH3CH2OH)2]n (TCZ-002), [Zn3(L27)2(DMA)6(CH3OH)]n (TCZ-003), [Cd3(L27)2(DMA)6(H2O)2]n (TCZ-004), and [Cd9(L27)6DMA13(4,4′-BPY)2(OH)2(H2O)13.5]n (TCZ-005) [H3L27 = 2,7-bis(4-benzoic acid)-N-(4-benzoic acid) carbazole, DMA = N,N-dimethylacetamide, 4,4′-BPY = 4,4′-bipyridine, TCZ = “T”-shape carbazole-based polymers, L27 = fully deprotonated H3L273− ligand]. All of the five CPs were assembled from a novel luminescent carbazole-based ligand. X-ray crystallography showed that TCZ-001 is a 3-connected one-dimensional (1D) chain structure with a {42·6} topology. TCZ-002 possesses a 3,6-connected three-dimensional (3D) framework with a point symbol of {42·6}2{44·62·87·102}. TCZ-003 displays a 3,6-connected two-dimensional 2D network with a Schläfli symbol of {411·64}·{43}2, which is a new topology. TCZ-004 features a 3,6-connected 2D net with a {43}2·{46·66·83} topology. In TCZ-005, the structure can be classified into two groups: one of the two groups is a 3-connected 1D chain structure with a {42·6} topology, similar to TCZ-001; the other one possesses a 3,3,3,4-connected network with a Schläfli symbol of {42·63·8}{42·6}3. The structure of TCZ-005 could be described as an SP 1-periodic net (4,4)(0,2) in the 1D_2D.ttd database. TCZ-001, TCZ-003 and TCZ-004 show a remarkable response to the Ni2+ concentration in DMA, H2O or EtOH. Some of Zn2+ ions were replaced by Ni2+ ions and the rate of the transmetalation depended on the concentration of Ni2+ ions. Also, changing part of the metal node would transform the colour of emitted light. Additionally, the colour of the luminescence displays a linear correlation with the Ni2+ concentration range from 0.005 to 0.35 M (mol L−1). Besides selective sensing of Ni2+, TCZ-004 can also be utilized to detect Eu3+ in DMA solution. Thus, several potential sensory probe materials for Ni2+ and Eu3+ detection in DMA solution have been obtained.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...