Single quantum dot-based nanosensor for rapid and sensitive detection of terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase†
Abstract
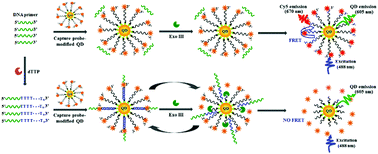
We developed a simple and rapid method for terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT) assay on the basis of the polymerization-directed exonuclease-assisted construction of a single quantum dot (QD)-based fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) nanosensor. This method is very sensitive with a detection limit as low as 1 × 10−6 U μL−1, and it can be used for the screening of TDT inhibitors and accurate quantification of TdT activity even in 5 cancer cells.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...