Heuristics for precise supramolecular control of soft matter structure and properties – 2,3,4-tris(dodecyloxy)benzenesulfonates with alkaline and organic cations
Abstract
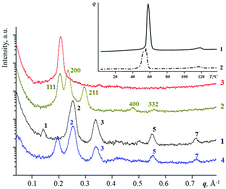
Comprehensive analysis of the structure and phase behavior for a number of 2,3,4-tris(dodecyloxy)benzenesulfonates with alkali metal and organic focal groups revealed that the shape of the mesogenic group plays a decisive role in phase behavior of the material. Cubic and layered types of packing prevail when the size of the cation is small and, thus, the shape of the mesogenic molecule is close to conic one. With increasing cation size, the shape becomes more tapered, and columnar mesophases appear to be more stable. Interactions of the focal groups however determine the stability of mesophases. Comparatively strong interactions may, morever, provide substantial deviations from a phase diagram plotting the transition temperatures versus the radius of focal group, as in the case of pyridinium 2,3,4-tris(dodecyloxy)benzenesulfonate.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...