Applications of particulate oxygen-generating substances (POGS) in the bioartificial pancreas
Abstract
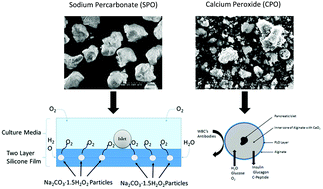
Type-1 Diabetes (T1D) is a devastating autoimmune disorder which results in the destruction of beta cells within the pancreas. A promising treatment strategy for T1D is the replacement of the lost beta cell mass through implantation of immune-isolated microencapsulated islets referred to as the bioartificial pancreas. The goal of this approach is to restore blood glucose regulation and prevent the long-term comorbidities of T1D without the need for immunosuppressants. A major requirement in the quest to achieve this goal is to address the oxygen needs of islet cells. Islets are highly metabolically active and require a significant amount of oxygen for normal function. During the process of isolation, microencapsulation, and processing prior to transplantation, the islets’ oxygen supply is disrupted, and a large amount of islet cells are therefore lost due to extended hypoxia, thus creating a major barrier to clinical success with this treatment. In this work, we have investigated the oxygen generating compounds, sodium percarbonate (SPO) and calcium peroxide (CPO) as potential supplemental oxygen sources for islets during isolation and encapsulation before and immediately after transplantation. First, SPO particles were used as an oxygen source for islets during isolation. Secondly, silicone films containing SPO were used to provide supplemental oxygen to islets for up to 4 days in culture. Finally, CPO was used as an oxygen source for encapsulated cells by co-encapsulating CPO particles with islets in permselective alginate microspheres. These studies provide an important proof of concept for the utilization of these oxygen generating materials to prevent beta cell death caused by hypoxia.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...