An in vivo study on bone formation behavior of microporous granular calcium phosphate
Abstract
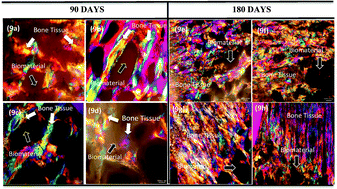
This study was developed based on in vivo investigation of microporous granular biomaterials based on calcium phosphates, involving matrices of β-tricalcium phosphate (β-TCP), hydroxyapatite (HA), biphasic compositions of both phases and a control group. The physicochemical characterization of materials was carried out by X-Ray diffraction (DRX) and mercury porosimetry. Biodegradability, bioactivity and neoformation processes were investigated by Raman spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and polarized light conducted on biopsies obtained from in vivo tests for periods of 90 and 180 days. These were performed to evaluate the behavior of granular microporous compositions in relation to bone neoformation. Through the performance obtained from in vivo assays, excellent osseointegration and bone tissue neoformation were observed. The results are encouraging and show that the microporous granular biomaterials of HA, β-TCP and biphasic compositions show similar results with perfect osseointegration. Architectures simulating a bone structure can make the difference between biomaterials for bone tissue replacement and repair.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...