Rapid and selective determination of melamine from eggs and milk based on magnetic surface molecularly imprinting technology†
Abstract
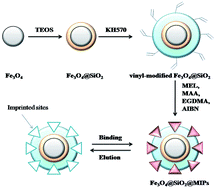
In this study, a rapid and selective method based on magnetic surface molecularly imprinting technology coupled with high performance liquid chromatography was used for the determination of melamine from egg and milk samples. A novel magnetic surface molecularly imprinted polymer (Fe3O4@SiO2@MIPs) with super-paramagnetic properties and high selectivity for melamine was synthesized as a magnetic adsorbent. The extraction, purification, and concentration processes were carried out simultaneously in a single step using an external magnet. The Fe3O4@SiO2@MIPs were characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM). The adsorption thermodynamics, kinetics, and selectivity were used to investigate the rebinding mechanism of the proposed polymers, which showed better affinity and selectivity as compared to Fe3O4@SiO2@NIPs. In addition, the matrix effect was evaluated. Various parameters, such as extraction solvent, pH of the solution, amount of the polymers, extraction time, washing conditions, and eluent, affecting the extraction efficiency were evaluated. The calibration curves show a satisfactory linear relationship (r = 0.9990–0.9997) in the linear range of 0.1–1000 ng g−1. The limit of detection (LOD) was 0.79 ng g−1 for milk and 0.43 ng g−1 for eggs. Recoveries ranging from 88.4 to 98.2% were obtained with the intra- and inter-day RSDs in the range of 3.5–5.4% and 5.7–7.8%, respectively. The proposed Fe3O4@SiO2@MIPs were successfully applied towards the selective determination of melamine in different real egg and milk samples, and satisfactory recoveries in the range from 87.9% to 102.4% with an RSD of less than 5.40% were obtained. The proposed method simplified the procedures of the classical solid-phase extraction (SPE) method and improved the reliability of the applied method.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...