Principal elementary mode analysis (PEMA)†
Abstract
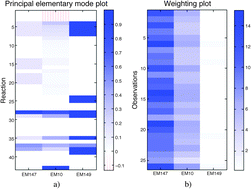
Principal component analysis (PCA) has been widely applied in fluxomics to compress data into a few latent structures in order to simplify the identification of metabolic patterns. These latent structures lack a direct biological interpretation due to the intrinsic constraints associated with a PCA model. Here we introduce a new method that significantly improves the interpretability of the principal components with a direct link to metabolic pathways. This method, called principal elementary mode analysis (PEMA), establishes a bridge between a PCA-like model, aimed at explaining the maximum variance in flux data, and the set of elementary modes (EMs) of a metabolic network. It provides an easy way to identify metabolic patterns in large fluxomics datasets in terms of the simplest pathways of the organism metabolism. The results using a real metabolic model of Escherichia coli show the ability of PEMA to identify the EMs that generated the different simulated flux distributions. Actual flux data of E. coli and Pichia pastoris cultures confirm the results observed in the simulated study, providing a biologically meaningful model to explain flux data of both organisms in terms of the EM activation. The PEMA toolbox is freely available for non-commercial purposes on http://mseg.webs.upv.es.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...