Bioactive polyphenol interactions with β amyloid: a comparison of binding modelling, effects on fibril and aggregate formation and neuroprotective capacity
Abstract
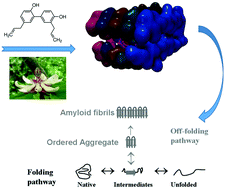
In this study we compared the effects of a diverse set of natural polyphenolics ligands on in silico interactive modelling, in vitro anti-aggregative properties and neuronal toxicity of β amyloid. The β amyloid-binding characteristics of optimised structural conformations of polyphenols with ascribed neuroprotective actions including punicalagin, myricetin, luteolin and honokiol were determined in silico. Thioflavin T and transmission electron microscopy were used to assess in vitro inhibitory effects of these polyphenols on Aβ1–42 fibril and aggregation formation. Phaeochromocytoma (PC12) cells were exposed to Aβ1–42, alone and in combination with test concentrations of each polyphenol (100 μM) and viability measured using MTT assay. Aβ1–42 evoked a concentration-dependent loss of cell viability in PC12 cells, in which all four polyphenols demonstrated significant inhibition of neurotoxicity. While all compounds variably altered the morphology of Aβ aggregation, the flavonoids luteolin and myricetin and the lignan honokiol all bound in a similar hydrophobic region of the amyloid pentamer and exerted the most pronounced inhibition of Aβ1–42 aggregation. Each of the polyphenols demonstrated neuroprotective effects in PC12 cells exposed to Aβ1–42, including punicalagin. These findings highlight some structure–activity insights that can be gleaned into the anti-aggregatory properties of bioactive polyphenols based on modelling of their binding to β-amyloid, but also serve to highlight the more general cellular neuroprotective nature of such compounds.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Alzheimer's Research Month 2016
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...