Non-fouling hyaluronic acid coatings for improved sandwich ELISA measurements in plasma†
Abstract
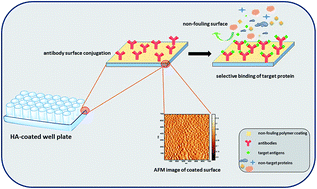
Nonspecific protein adsorption can interfere with blood diagnostics, especially in point-of-care tests for which minimal sample processing is required. Here we report a non-fouling coating material for presenting capture antibodies in ELISA that significantly increased precision and accuracy compared to a commercial ELISA microplates in human plasma and model solutions containing plasma proteins. The coating was prepared by functionalizing the hydrophilic polysaccharide hyaluronic acid (HA) with a thermoresponsive polymer, poly(di(ethylene glycol)) methyl ether methacrylate (PMEO2MA). Previous studies demonstrated that these coatings were resistant to adsorption of major blood proteins, and we demonstrate that functionalization of the coatings with a monoclonal antibody against tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) provided enhanced detection accuracy for this pro-inflammatory cytokine in ELISA. Three plasma-type solutions were explored in this work based either on buffer containing known concentrations of albumin, fibrinogen and immunoglobulin at sub-physiological and physiological concentrations, and non-diluted human plasma. In model solutions of plasma, even sub-physiological concentrations of plasma proteins resulted in a 20% overestimate of TNF-α concentration in the commercial ELISA kit but a 4% overestimate in HA-coated microwells. However, in human plasma, the commercial ELISA kit underestimated the analyte concentration by up to 95% while the HA-coated microwells did so by only 15% at an analyte concentration of 12.5 pg mL−1. The improvements in precision and accuracy provided by HA coatings suggests they could be used to enhance ELISA measurements in a broad range of complex biological media.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...