Self-reducible copper ion complex ink for air sinterable conductive electrodes†
Abstract
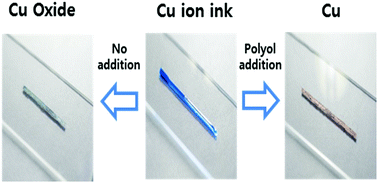
Copper (Cu) based conductive inks have been widely studied with the objective of achieving highly conductive and low-cost electrodes for various electrical devices. However, the unstable oxidation properties of Cu inks make them difficult to be applied for a wide range of practical applications. The oxidation properties induce high resistivity in the electrode fabrication, and storage problem of ink. Herein, we introduce a novel self-reducible Cu ion complex ink (Cu-ink), composed by formate, alkanolamine groups and poly alcohols, for the air sinterable, low-cost, environmentally friendly fabrication of Cu conductive electrodes. The air sinterable properties of this novel Cu-ink are induced by the self-reducing activity of the Cu-ink ligand decomposition and the reduction-assistance properties of the polyol solvents. In particular, among various polyol solvents, glycerol was found to be the most suitable reduction assistant-material because of its relatively abundant hydroxyl groups, good evaporation properties, and environmentally friendly solvents. Through investigation of the Cu-ink sintering temperature and glycerol contents, we obtained the Cu electrode films with a low resistivity of 17 μΩ cm at 350 °C under air sintering conditions. Furthermore, various practical characteristics such as excellent storage stability (of up to 4 weeks), enhanced adhesion properties, and flexible retention characteristics for up to 2000 bending times (R/R0 < 1.2, bending radius 20 mm) were also demonstrated for Cu electrode films.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...