Small molecules of chalcone derivatives with high two-photon absorption activities in the near-IR region†
Abstract
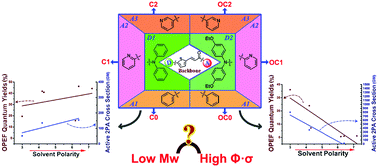
Designing small molecules with large two-photon absorption cross sections is urgently needed. In the present work, six novel chalcone thiophene derivatives were obtained by tuning the terminal electron-withdrawing/donating groups rationally. Their structure–property relationship was investigated both experimentally and theoretically. Crystallographic studies revealed that structural diversity was mainly influenced by ethyloxy groups. Both the alternation of electron-withdrawing/donating groups and the polarity of different solvents had a considerable influence on their photophysical properties. The results of UV-vis and one-/two-photon excited emission spectra showed that the high polarity solvents increased the quantum yields (Φ) and two-photon absorption cross-sections (σ) of type C chalcones, while they decreased those of type OC chalcones. It should be highlighted that as they are small molecules, favorable Φ and σ values were obtained. Finally, a preliminary attempt has been made in the biological imaging field, with satisfactory results that C-1 and OC-1 could locate uniformly in a cytosolic membrane-like system.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...