Chiral porous hybrid particles constructed by helical substituted polyacetylene covalently bonded organosilica for enantioselective release†
Abstract
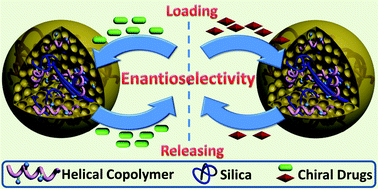
Hybrid materials are interesting because they combine the advantages of multiple components in one material entity. This article reports on a new type of chiral porous hybrid particle constructed by helical substituted polyacetylene and silica. To prepare the hybrid particles, chirally helical substituted acetylene copolymers containing pendent Si–O–Et groups were first synthesized and subsequently used as macromolecular silane couplers to perform a sol–gel reaction with TEOS. After aging, the designed hybrid particles were fabricated. Phase separation in the sol–gel reaction endowed the hybrid particles with abundant pores. In the resulting hybrid particles, inorganic silica constituted the rigid framework, whereas the organic helical substituted polyacetylene bonded with the framework and offered optical activity. SEM images confirmed the formation of spherical particles with regular morphology and porous structure. Circular dichroism and UV-vis absorption spectra demonstrated that the helical polymer chains had a preferential helicity and considerable optical activity in the hybrid particles. The hybrid materials demonstrated the capability of enantioselectively releasing cinchona alkaloid, which was used to model chiral drugs. The release process was found to be influenced by temperature: low temperature was more favorable for enantio-differentiating release.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...