Co-ZIF-9/TiO2 nanostructure for superior CO2 photoreduction activity†
Abstract
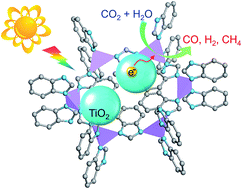
Cobalt-containing zeolitic imidazolate frameworks (Co-ZIF-9) have recently emerged as efficient imidazolate motifs for CO2 adsorption and activation. Herein, we adopt an imidazolate motif as a cocatalyst for TiO2 based CO2 photoreduction. Co-ZIF-9/TiO2 (denoted as ZIFx/T) composite materials were firstly synthesized via an in situ synthetic procedure, and this endowed the fabricated ZIFx/T composites with a well-designed nanostructure in which TiO2 and Co-ZIF-9 were closely bound with each other, thus leading to better charge separation compared to the previously reported physical mixture of ZIF with other semiconductors. Via optimization of the concentration of Co-ZIF-9 in the ZIFx/T composites, 8.79 μmol of CO, 0.99 μmol of CH4, and 1.30 μmol of H2 with a total utilized photoelectron number (UPN) of 28.17 μmol could be obtained over ZIF0.03/T after 10 h of CO2 photoreduction, which is about 2.1 times that of pure TiO2. Linear sweep voltammetry at the pseudo stationary state in a CO2 saturated solution further revealed that Co-ZIF-9 can effectively activate the CO2 molecule and positively shift the onset potential of CO2 reduction for ZIFx/T (x ≤ 0.10). Moreover, photoluminescence spectra suggest that the ZIFx/T composites prepared via the in situ synthetic procedure have better charge separation efficiency with less Co-ZIF-9 content. Accordingly, both better CO2 activation and charge separation contribute to the high activity of the well-designed ZIFx/T nanostructure.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...