Ab initio modelling of oxygen vacancies and protonic defects in La1−xSrxFeO3−δ perovskite solid solutions†
Abstract
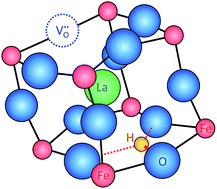
Using hybrid density functionals, detailed ab initio calculations were performed for oxygen vacancies and protons in La1−xSrxFeO3−δ perovskite solid solutions which may serve as a cathode material in protonic ceramic fuel cells. The atomic and electronic structures of different configurations of defects and the role of Fe oxidation state are analyzed in detail. The energetics of the reduction and hydration reactions are investigated. The hydration energy is found to be significantly smaller than for Ba(Zr1−xYx)O3−x/2 electrolyte materials, and the role of basicity as one decisive factor is discussed.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...