N-Annulated perylene substituted zinc–porphyrins with different linking modes and electron acceptors for dye sensitized solar cells†
Abstract
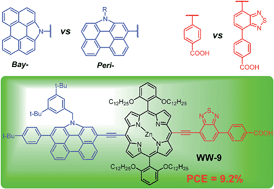
Three new N-annulated perylene (NP) substituted porphyrin dyes WW-7–WW-9 with different linking modes and accepting groups were synthesized and applied in Co(II)/(III) based dye sensitized solar cells (DSCs). The bay-linked porphyrins WW-7 and WW-8 exhibited moderate power conversion efficiency (PCE = 4.4% and 4.8%, respectively), while the peri-linked porphyrin dye WW-9 showed a PCE up to 9.2% which is slightly lower than that of our reference dye WW-6. Detailed physical measurements (optical and electrochemical), DFT calculations, and photovoltaic characterizations were performed to understand how the structural changes affect their light-harvesting ability, molecular orbital profile, energy level alignment, and eventually the photovoltaic performance. It turned out that the lower efficiencies of the cells based on WW-7 and WW-8 could be ascribed to the weak π-conjugation between the bay-substituted NP and phenylethynyl substituted porphyrin unit. The introduction of a benzothiadiazole acceptor at the anchoring group has induced a significant red shift of the IPCE action spectra of WW-8 and WW-9, by about 90 nm and 50 nm as compared to that of WW-7 and WW-6, respectively. However, less efficient electron injection was observed. Our studies gave some insight into the important role of electronic interactions between different components when one designs a dye for high-efficiency DSCs.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...