Effect of a MoO3 buffer layer between C8-BTBT and Co(100) single-crystal film
Abstract
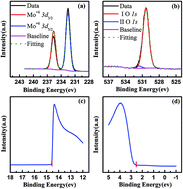
The effect of a MoO3 buffer layer inserted between 2,7-dioctyl[1]benzothieno[3,2-b]benzothiophene (C8-BTBT) and Co single-crystal film has been investigated using X-ray photoemission spectroscopy (XPS) and ultraviolet photoemission spectroscopy (UPS). The high work function of the MoO3 buffer layer bends the electronic structure of C8-BTBT upward toward the interface, and thus reduces the hole injection barrier to 0.97 eV, facilitating the hole injection from the Co electrode to C8-BTBT via electron extraction from the highest occupied molecular orbital of C8-BTBT through the low-lying conduction band of MoO3. Desulfurization reaction of C8-BTBT by cobalt is also eliminated by the MoO3 buffer layer. These effects illustrate the significance of a MoO3 buffer layer on interface energy level alignment and provide important insight into device design, fabrication and possible direction to improve the performance of C8-BTBT/Co-based organic spin valves.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...