Copper-modified TS-1 catalyzed hydroxylation of phenol with hydrogen peroxide as the oxidant
Abstract
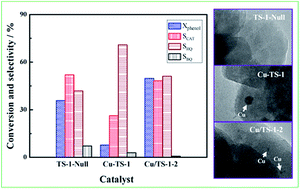
Herein, TS-1, Cu incorporated TS-1 (Cu–TS-1) and TS-1 supported with different Cu contents (Cu/TS-1-x) are synthesized. The resultant catalyst samples are characterized via X-ray powder diffraction (XRD), nitrogen physical adsorption (N2-adsorption), inductive coupling plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), ultraviolet-visible diffuse reflectance (UV-vis) spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), and studied in the hydroxylation of phenol using H2O2 as the oxidant. The results reveal that the framework Ti content and particle diameter of the Cu/TS-1-x samples are almost the same as the untreated TS-1 sample, and that active Cu2+ species exist on the catalyst surface. However, the framework Ti of the Cu–TS-1 sample is lost and its particle size increases. This feature may be attributed to the fact that a small amount of Cu species is introduced into the TS-1 framework, which inhibits the formation of framework Ti. Furthermore, the Cu/TS-1-2 catalyst exhibits the best catalytic activity due to the existence of framework Ti and Cu2+ species which can promote the conversion of phenol. Furthermore, the phenol conversion of 49.77% and diphenol selectivity of 99.28% are obtained when phenol hydroxylation is carried out at 353 K for 3 h over this catalyst.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...