Improved performance of dye-sensitized solar cells based on modified kaolin/PVDF-HFP composite gel electrolytes
Abstract
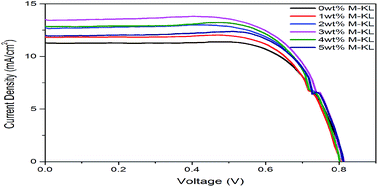
Dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs) fabricated with poly(vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene) (PVDF-HFP) composite gel electrolytes containing variable amounts of modified kaolin were studied in this work. The kaolin was modified with silane coupling agent γ-aminopropyltriethoxysilane (KH550), and the modified kaolin (M-KL) was characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). The results of X-ray diffraction (XRD) and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) indicated that the crystallinity of polymer membranes decreased with the addition of M-KL nanoparticles. The ionic conductivity and diffusion coefficient (I3−) of polymer gel electrolytes (PGEs) reached optimum values of 9.452 × 10−3 S cm−1 and 10.37 × 10−6 cm2 s−1 for 3 wt% M-KL, respectively, which contributed to higher short-circuit current density (Jsc) and photoelectric conversion efficiency (η) of the corresponding DSSCs. The optimum level of η reached 7.48% under the illumination of 100 mW cm−2, an increase of 16.3% compared with the DSSC without M-KL.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...