Cellulose-based spreadable new thixo gels: synthesis and their characterization†
Abstract
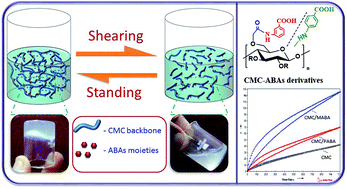
Carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) based new thixotropic gels were synthesized by a facile microwave-induced reaction of aminobenzoic acids (ABAs) e.g. para- and meta-aminobenzoic acids. Cellulose of the halophytic plant Salicornia brachiata was employed in this investigation. These derivatives were characterized by FT-IR, 13C NMR spectra, thermal analyses and surface morphology studies. These compounds form thixotropic soft gels in water, which were evaluated by rheological measurements. Their antioxidant properties were estimated by in vitro DPPH radical scavenging assay. These CMC-based new materials would be of potential utility in spreadable formulations in personal care applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...