Polyethylene glycol/Cu/SiO2 form stable composite phase change materials: preparation, characterization, and thermal conductivity enhancement
Abstract
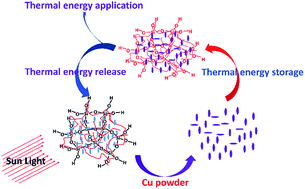
Novel form-stable composite phase change materials (FS-CPCMs) of polyethylene glycol (PEG)/Cu/SiO2 were prepared by adding Cu powder to PEG and SiO2 via the ultrasound-assisted sol–gel method. This method ensured the uniform distribution of Cu powder in the FS-CPCMs, thus providing an important method to develop composite phase change materials (CPCMs) with a high thermal conductivity. The FS-CPCMs were characterized by various techniques. The results showed that the FS-CPCMs remained in the solid state without leakage above the melting point of PEG. The XRD and FTIR results indicated that no new chemical bond was formed between the constituents of FS-CPCMs: Cu, PEG, and SiO2. The DSC and TGA analyses showed that the FS-CPCMs had an optimum phase-change temperature, a high enthalpy of phase change, an excellent thermal stability, and a good form-stable performance. The thermal conductivity was 0.431 W m−1 K−1 for 3.45 wt% Cu powder in the FS-CPCMs, an increase of 49.13% compared to pure PEG.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...