Synthesis and characterization of chitosan–zinc composite electrodeposits with enhanced antibacterial properties
Abstract
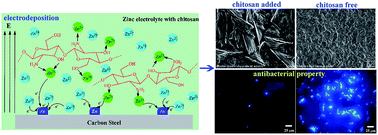
Zinc electrodeposits are one of the most popular safeguard procedures for steel constructions. However, in natural aquatic environments, especially marine environments, zinc electrodeposits suffer significantly from microbial induced corrosion and biofouling which lead to metal failure. To better confront the microbial induced problems, a biocide-zinc electrodeposit was synthesized based on chelating action. In this paper, nontoxic and biocidal natural polysaccharide, chitosan, was successfully incorporated into the zinc electrodeposit matrix, synthesizing a kind of chitosan–zinc composite electrodeposit. The addition of chitosan in the electrolyte influenced the surface morphology and crystalline structure of the resultant electrodeposits significantly, while a chitosan–zinc chelation complex was also found in the electrodeposits. A synthesis model was proposed in which a chitosan molecule could chelate zinc ions in the electrolyte by means of its N atoms in amino groups and O atoms in hydroxide radicals, which promoted the codeposition of zinc and chitosan during synthesis. Furthermore, remarkably enhanced broad-spectrum bactericidal properties of the chitosan–zinc electrodeposits were revealed through Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Shewanella oneidensis exposure. The best antibacterial properties of the resultant electrodeposits were obtained when the chitosan concentration was 0.6 g L−1 in the electrolyte.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...