Multicomponent sequential polymerizations of alkynes, carbonyl chloride and amino ester salts toward helical and luminescent polymers
Abstract
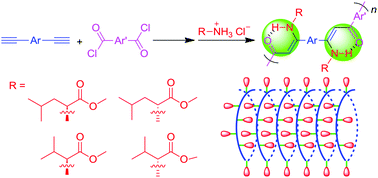
Multicomponent sequential reactions have recently received much attention owing to their outstanding advantages, such as simple operation, atom economy, and environmental benefit. In this work, we report a new multicomponent sequential reaction and the corresponding multicomponent sequential polymerization approach to construct conjugated structures with advanced functionalities. By employing 1,8-diazabicyclo[5.4.0]undec-7-ene as an additive, alkynes, carbonyl chloride and amino ester salts undergo a one-pot three-component sequential reaction successfully. Similarly, the derived multicomponent sequential polymerizations of diyne, terephthaloyl chloride and amino ester proceed smoothly in a regio- and stereoregular manner and generate conjugated nitrogen-substituted poly(enaminone)s with high molecular weights in satisfactory yields. All the resulting polymers are soluble in common solvents, and possess high thermal stability and good film-forming ability. Interestingly, the incorporation of optically active chiral amino esters as pendants leads to polymeric products with helical rotating backbones, as revealed by their circular dichroism spectra in the solutions and as cast films. With fluorescent tetraphenylethene moieties embedded in the polymer chains, the polymers display a phenomenon of aggregation-enhanced emission. They emit weakly in the solution state, but fluoresce intensely as aggregates. Moreover, the thin films of the polymers exhibit high light refractivity (n = 1.9305–1.5992) in a wide wavelength region (400–1000 nm), which can be readily modulated by UV irradiation. Additionally, the polymeric products with photosensitivity can generate highly resolved two-dimensional luminescent patterns by UV treatment.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...