g-C3N4 modified flower-like WO3–Bi2WO6 microspheres with enhanced photoelectrocatalytic activity
Abstract
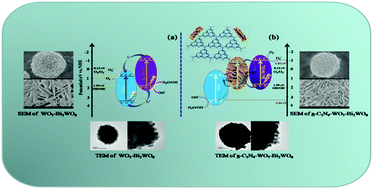
Graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4) modified flower-like WO3–Bi2WO6 microspheres were prepared by hydrothermal and thermo polymerization methods. The as-prepared samples were characterized by X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, high-resolution transmission electron microscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. The photoelectrocatalytic activity of all samples was evaluated by decomposition of methyl orange (MO) and phenol under visible light illumination. The photoelectrochemical test and analysis of energy-band theory showed that the photogenerated electrons (e−) and holes (h+) had strong reducing capability and oxidation capability, respectively, compared with WO3–Bi2WO6 heterojunction energy-band theory. The photoelectrocatalytic activity of g-C3N4 modified WO3–Bi2WO6 was higher than that of pure g-C3N4 and WO3–Bi2WO6, which attributed to the efficient visible-light and electricity utilization efficiency and the construction of the double Z-scheme. The g-C3N4 served as a charge transmission bridge between the WO3 and the Bi2WO6, and the Z-scheme kept the electrons with high reducing capability in the conduction band (CB) of Bi2WO6 and the holes with high oxidation capability in the valence band (VB) of WO3. Meanwhile, the influence of the g-C3N4 amount on photoelectrocatalytic activity was discussed in detail. It was found that the optimal amount of g-C3N4 was 5 wt% in the double Z-scheme system, which demonstrated excellent photoelectrocatalytic activity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...