Design, synthesis and relaxation studies of triazole linked gadolinium(iii)–DO3A-BT-bistriazaspirodecanone as a potential MRI contrast agent†
Abstract
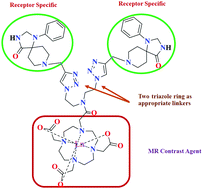
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a diagnostic and research technique widely used in clinical research. We describe here a novel and facile synthesis of a bisconjugated triazaspirodecanone moiety using ‘click chemistry’ as a key step in the synthesis of a triazole based macrocyclic MRI contrast agent. A bivalent approach has been applied to conjugate two triazole rings and triazaspirodecanone moieties across a four carbon spaced linker which is finally conjugated to DO3A to yield the desired MRI contrast agent, DO3A-bis(triazole-triazaspirodecanone), in an overall yield of 70%. All the intermediates and the final compounds have been characterized by NMR and mass spectrometry. In vitro experiments include cytotoxicity (MTT assay) and relaxivity studies. The potentiometric titration of a gadolinium loaded complex displayed strong selectivity for Gd3+ over physiological metal ions such as Zn2+ and Cu2+. IC50 values obtained from the MTT assay indicate the suitability of the synthesized conjugate as a safe diagnostic agent. The longitudinal relaxivity of DO3A-bis(triazole-triazaspirodecanone) was found to be 18.6 mM−1 s−1, which shows that the synthesized conjugate is a suitable MRI contrast agent.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Nitrogen Ligands

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...