Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of pyrazoline nucleus based homoleptic Ru(iii) compounds†‡
Abstract
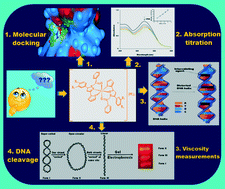
A series of tri-substituted pyrazoline nucleus based homoleptic Ru(III) complexes of type [Ru(L1–7)2]·(PF6)3 (L1–7= heterocyclic pyrazoline derivatives) were synthesized and characterized by elemental analysis, their electronic spectra, conductance measurements, thermo gravimetric analysis (TGA), electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR), Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy and mass spectrometry (MS). An octahedral geometry around ruthenium was assigned in all complexes using electronic spectral analysis and EPR measurements. All compounds were evaluated for cytotoxicity activity against S. pombe cells at a cellular level. A comparative study of cellular level cytotoxicity values of all the compounds indicated that all the metal complexes showed better activity against S. pombe cells compared to the free heterocyclic pyrazoline ligand. All the complexes were good in vitro cytotoxic agents and LC50 values were in the 5.57–8.01 mg L−1 range. They were also screened for their in vitro antimicrobial behavior against five different microorganisms. Inspection of their interaction with Herring Sperm (HS) DNA with an absorption titration (Kb = 0.37–5.02 × 105 L mol−1) and viscosity measurement study and suggested the classical intercalative mode of DNA binding. Moreover, the DNA-binding property of all the compounds were examined theoretically using a molecular docking study and suggested an intercalation binding mode between complex and nucleotide base pairs of DNA. The cleavage study on pUC19 DNA was checked by agarose gel electrophoresis. All newly synthesized compounds were also evaluated for their in vitro antimalarial study against the Plasmodium falciparum strain (IC50 = 0.46–1.50 mg L−1).

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...