Bacterial lipid membranes as promising targets to fight antimicrobial resistance, molecular foundations and illustration through the renewal of aminoglycoside antibiotics and emergence of amphiphilic aminoglycosides†
Abstract
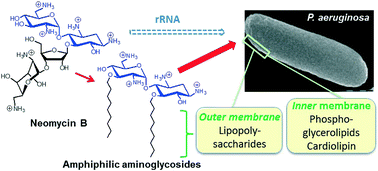
Hereunder, we highlight bacterial membrane anionic lipids as attractive targets in the design of antibacterial drugs which can be effective against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative resistant bacteria. In this approach, first, molecular foundations and structure–activity relationships are laid out for membrane-targeting drugs and drug candidates from the structure and physicochemical properties of the main membrane targets, describing, as well, the corresponding identified resistances. Second, this approach is illustrated by the history of the emergence of antibacterial and antifungal amphiphilic aminoglycosides (AAGs) which are active against Gram-positive and Gram-negative resistant bacteria. AAGs have resulted from intensive medicinal chemistry development of a group of old antibiotic drugs known as aminoglycosides (AGs), which target ribosomal RNA. The aforementioned AAG's are being used towards discovering new antibiotics which are less toxic and less susceptible to resistance. The recent results in the field of AAGs are described and discussed in terms of structure–activity relationships and mechanism of action.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...