Digital microfluidics for spheroid-based invasion assays
Abstract
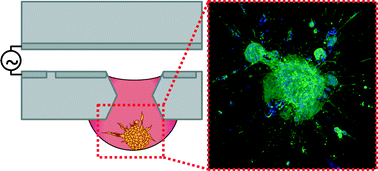
Cell invasion is a key process in tissue growth, wound healing, and tumor progression. Most invasion assays examine cells cultured in adherent monolayers, which fail to recapitulate the three-dimensional nuances of the tissue microenvironment. Multicellular cell spheroids have a three-dimensional (3D) morphology and mimic the intercellular interactions found in tissues in vivo, thus providing a more physiologically relevant model for studying the tissue microenvironment and processes such as cell invasion. Spheroid-based invasion assays often require tedious, manually intensive handling protocols or the use of robotic liquid handling systems, which can be expensive to acquire, operate, and maintain. Here we describe a digital microfluidic (DμF) platform that enables formation of spheroids by the hanging drop method, encapsulation of the spheroids in collagen, and the exposure of spheroids to migration-modulating agents. Collagen sol–gel solutions up to 4 mg mL−1, which form gels with elastic moduli up to ∼50 kPa, can be manipulated on the device. In situ spheroid migration assays show that cells from human fibroblast spheroids exhibit invasion into collagen gels, which can be either enhanced or inhibited by the delivery of exogenous migration modulating agents. Exposing fibroblast spheroids to spheroid secretions from colon cancer spheroids resulted in a >100% increase in fibroblast invasion into the collagen gel, consistent with the cancer-associated fibroblast phenotype. These data show that DμF can be used to automate the liquid handling protocols for spheroid-based invasion assays and create a cell invasion model that mimics the tissue microenvironment more closely than two-dimensional culturing techniques do. A DμF platform that facilitates the creation and assaying of 3D in vitro tissue models has the potential to make automated 3D cell-based assays more accessible to researchers in the life sciences.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...